Doberman VC — Research Note
Topic: Cryptocurrency Tax Guide 2025: Comparative Global Overview, Legal Optimization, and Investor Playbook
Date: October 7, 2025
Executive Summary
- Tax landscape polarization accelerates: While crypto-friendly jurisdictions like UAE (0%), Germany (0% >12 months), and Portugal (0% >12 months) maintain zero-tax environments, high-tax countries intensify enforcement—Japan reaches 55%, Italy plans 42% increases, and the US implements comprehensive 1099-DA reporting from 2026.[1][2][3]
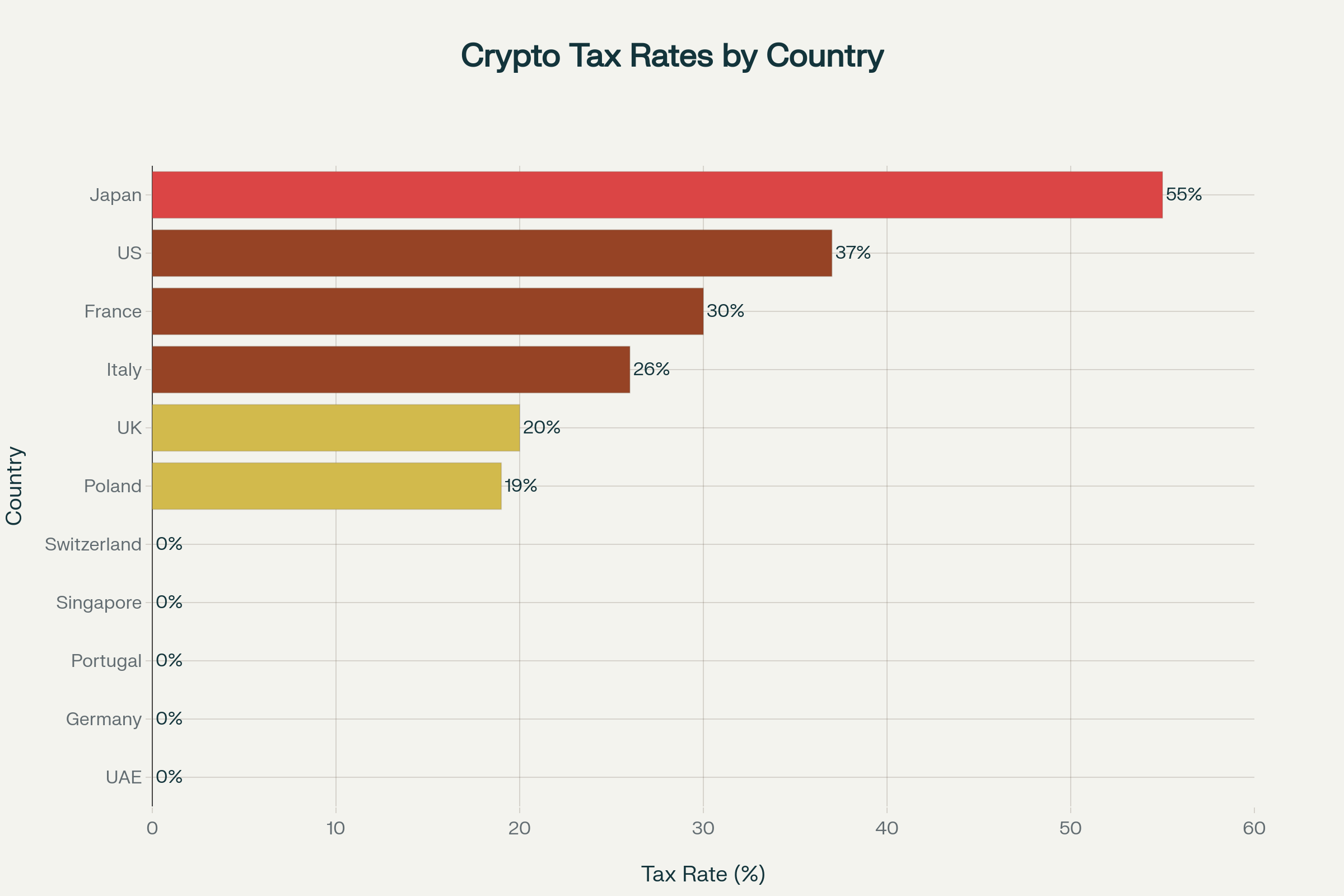
Global Cryptocurrency Tax Rates by Country (2025): Tax-Friendly vs High-Tax Jurisdictions
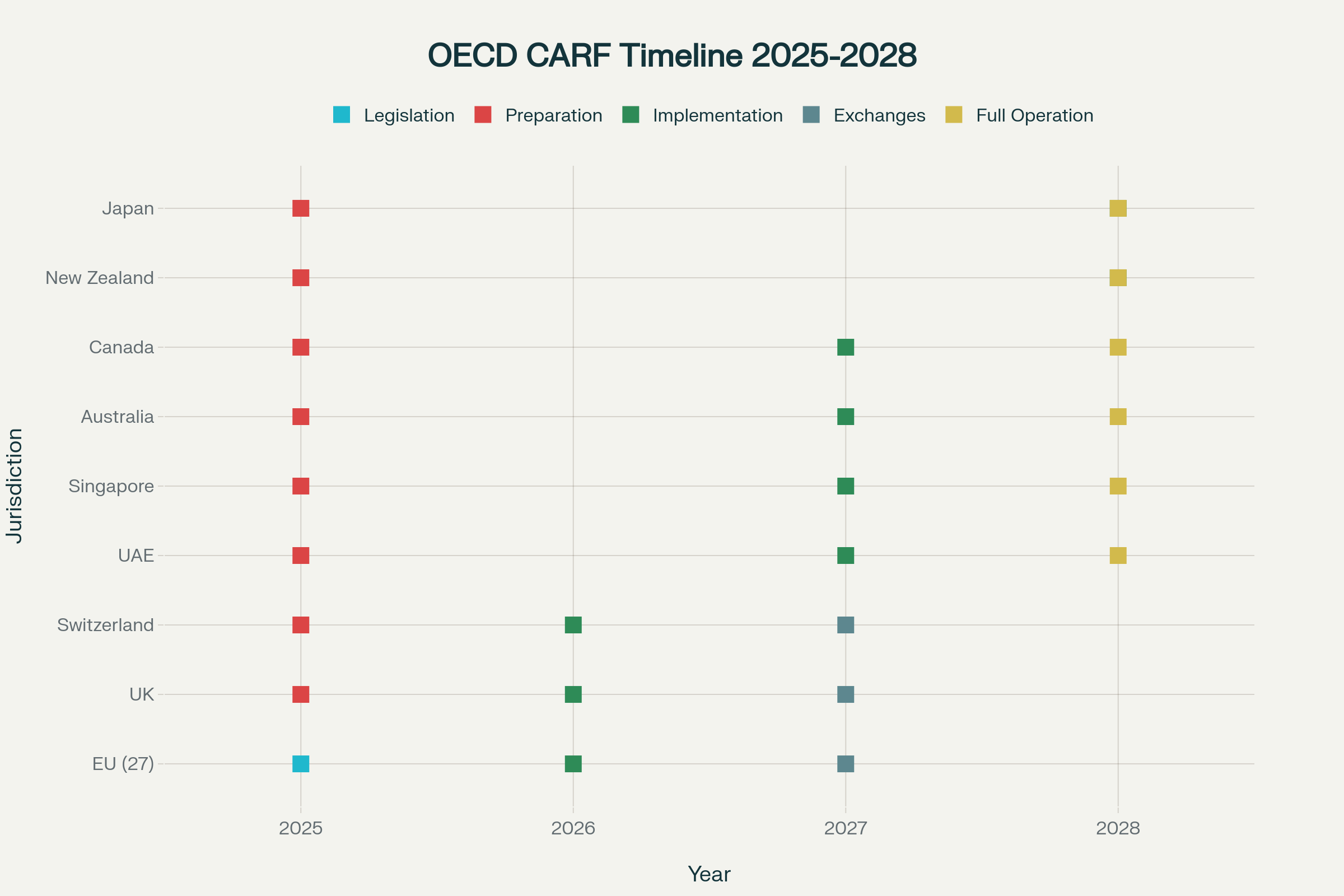
- OECD CARF transforms global transparency: 67 jurisdictions commit to automatic crypto data exchange by 2027-2028, ending traditional tax haven anonymity and requiring comprehensive reporting from all crypto service providers.[4][5][6]
Want the live signals behind this research?
Doberman VC tracks ETF flows, CME basis, stablecoin liquidity, BTC.D and rotation signals in real time. Get dashboards, alerts and weekly OSINT briefs.
OECD CARF Implementation Timeline (2025-2028): Global Crypto Tax Transparency Initiative
- Optimization window narrowing but viable: Strategic residency planning to UAE/Portugal pre-disposal, 12-month holding periods in Germany/Australia, and sophisticated wallet segregation remain effective, but require urgent implementation before CARF enforcement.[7][8][2:1]
- Biggest risk: Retroactive compliance enforcement as tax authorities gain CARF visibility into historical transactions; Biggest opportunity: immediate relocation to zero-tax jurisdictions for high-volume investors before 2027 reporting commences.[4:1][9]
- Critical threshold: investors with >$1M crypto portfolios should prioritize residency optimization now, while smaller holders (<$100K) can focus on holding period strategies and loss harvesting in their home jurisdictions.


Introduction & 2025 Landscape
The cryptocurrency tax environment underwent dramatic transformation in 2025, driven by three converging forces: the OECD’s Crypto-Asset Reporting Framework (CARF) implementation, expanded national enforcement capabilities, and institutional adoption requiring clear compliance frameworks.
Key 2025 Developments:
- CARF Rollout: 67 jurisdictions signed multilateral agreements for automatic crypto data exchange starting 2027-2028[5:1]
- Enhanced Reporting: US introduces Form 1099-DA for all crypto transactions from 2026; EU implements DAC8 by December 2025[10][3:1]
- Regulatory Clarity: UAE adopts comprehensive CARF framework while maintaining 0% individual tax rates; Portugal solidifies 12-month exemption rules[11][6:1]
The era of crypto tax anonymity is ending, but strategic opportunities remain for compliant optimization through jurisdictional arbitrage and holding period management.[4:2][8:1]
Defining Taxable Events
Universal Taxable Events (Most Jurisdictions)
- Crypto-to-fiat sales: Always taxable as capital gains or income
- Crypto-to-crypto trades: Taxable in US, UK, most EU countries; exempt in Portugal for pure swaps
- Spending crypto: Treated as disposal triggering capital gains calculations
- Mining income: Taxable as ordinary income at fair market value upon receipt
- Staking rewards: Generally taxable as income, with variations in timing recognition
Jurisdiction-Specific Variations
- Airdrops: Germany exempts “passive” airdrops but taxes those requiring user action; US taxes all airdrops as income[12][13]
- DeFi transactions: UK treats lending/staking as taxable disposals; Germany applies private asset rules with 12-month exemptions[14][15]
- NFT trading: Generally follows crypto rules but Germany may exempt >12-month holdings[13:1]
Professional Trader Classification: Crossing into business/professional status triggers higher tax rates and additional compliance obligations across all jurisdictions—critical threshold varies by trading frequency and income dependency.[16][17]
Tier-1 Jurisdictions: Advanced Tax Systems
United States
Classification: Property under IRC guidelines
Rates: 0-20% long-term capital gains (>12 months), 10-37% short-term/ordinary income
Reporting: Form 8949 for all disposals, Schedule D for net gains/losses, new Form 1099-DA from 2026
International obligations: FBAR for foreign accounts >$10K, Form 8938 for specified foreign assets >$50K/$200K thresholds[18][19][20]
Optimization strategies: Tax-loss harvesting (watch wash-sale rules), long-term holding for preferential rates, strategic timing around income brackets
Germany
Classification: Private money (not capital asset)
Rates: 0% for >12-month holdings, up to 45% income tax for <12-month disposals exceeding €600 annual threshold
Unique rules: Passive airdrops tax-free, active airdrops taxable as income, staking extends holding period requirement[21][12:1][22][13:2]
Key advantage: Complete tax exemption for disciplined long-term holders makes Germany optimal for accumulation phase strategies
United Kingdom
Classification: Asset subject to capital gains tax
Rates: 10% (basic rate taxpayers), 20% (higher rate taxpayers)
Annual exemption: £3,000 for 2025 tax year
DeFi complexity: Lending/staking treated as taxable disposals, returns classified as capital or income based on specific circumstances[14:1][15:1]
Switzerland
Classification: Private capital gains generally tax-exempt
Rates: 0% for private investors, progressive income tax for professional traders
Cantonal variations: Some cantons impose wealth tax on crypto holdings
CARF compliance: Implementing from 2026 with mandatory service provider registration[23]
Tier-2 Jurisdictions: Emerging Opportunities
United Arab Emirates
Classification: Complete individual tax exemption
Rates: 0% for individuals, 9% corporate tax on business income >375,000 AED ($102K)
2025 changes: CARF implementation from 2027 with comprehensive reporting requirements but tax rates unchanged
Optimization: Ideal for high-volume disposals, requires legitimate residency establishment[2:2][6:2][24]
Portugal
Classification: Asset taxation with holding period benefits
Rates: 28% for <12-month holdings, 0% for >12-month holdings
Crypto-to-crypto: Exempt from taxation, providing swap advantages
NHR program: Additional benefits for qualifying tax residents[11:1][7:1][2:3]
Poland
Classification: Property subject to flat capital gains tax
Rates: 19% flat rate with loss carry-forward provisions
Compliance: Moderate reporting requirements, EU CARF implementation from 2026[1:1]
Estonia
Classification: Progressive approach with business-friendly crypto policies
Rates: 20% capital gains tax, competitive for Baltic region
Corporate benefits: Attractive for crypto businesses with deferred taxation on retained earnings
Legal Optimization Strategies
Holding Period Arbitrage
Mechanism: Exploit jurisdictions offering reduced/zero rates for longer holding periods
Best countries: Germany (0% >12 months), Portugal (0% >12 months), Australia (50% discount >12 months)
Implementation: Plan disposals around holding period thresholds, segregate long/short-term positions[21:1][2:4]
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Mechanism: Realize losses to offset taxable gains within same tax year
Applicable jurisdictions: US, UK, Canada, most EU countries with loss offset provisions
Limitations: Watch wash-sale rules (US), ensure “same day” rule compliance (UK)
Timing: Execute in Q4 to maximize current-year benefit[18:1]
Strategic Residency Planning
High-impact jurisdictions: UAE (0% individual rates), Singapore (0% for private investors), Portugal (0% >12 months)
Requirements: Establish genuine residency (>183 days, local address, economic ties) before major disposals
Timeline: Plan 12-24 months ahead of significant exit events
Compliance: Maintain detailed residency documentation for tax authority scrutiny[8:2][2:5][24:1]
Business Structure Optimization
UAE Free Zones: 0-9% corporate tax rates for qualifying income with operational substance requirements
Malta: 0-35% progressive rates with EU access and favorable crypto regulatory environment
Cayman Islands: No capital gains, income, or corporate tax but enhanced CRS/CARF reporting obligations[2:6][25]
CARF Impact & Compliance Requirements
Implementation Timeline
- 2025: Final legislation in EU jurisdictions, public consultations in others
- 2026: Data collection begins, service provider registration mandatory
- 2027: First automatic exchanges commence (67 participating jurisdictions)
- 2028: Full global implementation and enforcement escalation[5:2]
Reporting Obligations
Crypto service providers must report:
- Customer identity verification and tax residency
- Transaction histories including dates, amounts, counterparties
- Account balances and cryptocurrency holdings
- Cross-border transfers and exchange activities[4:3][10:1][23:1]
Taxpayer implications:
- End of “anonymous” crypto transactions for most jurisdictions
- Historical transaction reconstruction may be required
- Enhanced audit risk for undeclared positions[6:3][4:4]
Strategic Responses
- Immediate: Complete historical compliance reviews and voluntary disclosures where beneficial
- Medium-term: Implement compliant record-keeping systems and professional tax advisory relationships
- Long-term: Consider jurisdictional optimization before enhanced enforcement begins[9:1]
Investor Practical Guide
Documentation Requirements
Universal essentials:
- Complete transaction logs with timestamps, amounts, exchange rates
- Proof of acquisition costs (exchange receipts, bank statements)
- Wallet addresses and private key custody documentation
- Annual snapshots for portfolio valuation purposes[19:1][20:1]
Record-Keeping Best Practices
Segregation strategies:
- Separate wallets for different tax treatments (mining, staking, long-term holds)
- Distinct addresses for business vs. personal activities
- Clear labeling system for cost basis tracking methods (FIFO, LIFO, specific identification)[3:2]
Filing Strategies by Jurisdiction
United States:
- Form 8949: Individual transaction reporting
- Schedule D: Summary gains/losses
- FBAR/Form 8938: Foreign account reporting
- Estimated payments: Quarterly for significant gains[19:2][20:2][26]
Germany:
- Anlage SO: Private disposal transactions
- Maintain 12-month holding documentation
- Distinguish business vs. private activity[12:2][22:1]
United Kingdom:
- Self Assessment (SA100): Annual return
- Capital Gains Summary (SA108): Crypto disposals
- Real-time reporting for large disposals[14:2]
Common Compliance Pitfalls
- Mixing business/personal wallets: Creates classification confusion and audit risk
- Incomplete cost basis records: Triggers unfavorable presumptions in audits
- Ignoring small transactions: “De minimis” rules vary by jurisdiction
- Staking/DeFi timing errors: Incorrect recognition dates inflate tax liability[20:3][12:3]
Risk Assessment & Mitigation
Primary Risk Factors
Regulatory retroactivity: Some jurisdictions may apply new rules to historical transactions, particularly for previously undisclosed activities.[9:2]
Professional trader reclassification: Excessive trading frequency can trigger business tax treatment with higher rates and social contribution obligations.[16:1][17:1]
CARF enforcement acceleration: Tax authorities gaining historical transaction visibility may trigger enhanced audit activity from 2027.[4:5][6:4]
Banking compliance integration: Crypto inflows increasingly flagged by financial institutions for source verification and tax compliance.[9:3]
Mitigation Strategies
Voluntary disclosure programs: Where available, can reduce penalties and provide compliance certainty for historical positions.[9:4]
Professional advisory relationships: Essential for complex positions, international structures, and ongoing compliance optimization.[8:3]
Diversified jurisdictional approach: Avoid concentration in single tax regime; maintain flexibility for changing regulatory environments.
Strategic Recommendations by Investor Profile
High-Volume Investors (>$1M portfolios)
Immediate actions:
- Conduct comprehensive compliance review of historical transactions
- Evaluate immediate residency optimization opportunities (UAE, Singapore, Portugal)
- Implement sophisticated wallet segregation and documentation systems
- Engage specialized crypto tax advisory services[8:4][24:2][9:5]
Moderate Investors ($100K-$1M portfolios)
Optimization focus:
- Maximize holding period benefits where applicable (Germany, Portugal, Australia)
- Implement tax-loss harvesting strategies in home jurisdiction
- Maintain detailed records for CARF compliance preparation
- Consider residency optimization for major exit events[2:7]
Retail Investors (<$100K portfolios)
Efficient compliance:
- Focus on holding period optimization in home jurisdiction
- Use automated tax calculation software for record-keeping
- Implement simple wallet segregation for different tax treatments
- Maintain compliance with existing reporting requirements
Conclusion & Forward Outlook
The cryptocurrency tax landscape in 2025 presents a final optimization window before comprehensive global transparency takes effect. While CARF implementation eliminates traditional tax haven secrecy, significant arbitrage opportunities remain through strategic residency planning, holding period management, and sophisticated compliance structuring.
Critical timeline: Investors have approximately 18-24 months to implement optimized structures before enhanced enforcement capabilities fully materialize. The jurisdictions offering genuine tax advantages—UAE, Germany for long-term holders, Portugal, Singapore—will likely face increased scrutiny but continue providing lawful optimization opportunities for compliant taxpayers.
Success factors: Professional advisory relationships, meticulous documentation, and proactive compliance positioning will differentiate successful crypto tax strategies from those facing retroactive enforcement actions. The era of casual crypto tax management is ending; institutional-grade compliance is now essential for material positions.
Appendix
Visual
- Chart 1: Global Cryptocurrency Tax Rates by Country (2025)
- Chart 2: OECD CARF Implementation Timeline (2025-2028)
Data Matrices
- Table 1: Tier 1 Countries Tax Comparison
- Table 2: Tier 2 Countries Tax Comparison
- Table 3: Taxable Events by Jurisdiction
- Table 4: Tax Optimization Strategies
Sources
Primary: OECD CARF documentation, national tax authority guidelines (IRS, HMRC, BMF, etc.), official government publications, PWC Tax Summaries
Secondary: Professional services firm analyses, crypto tax software providers, jurisdiction-specific legal analyses
All tax rates and regulations verified through official government sources as of October 2025. Given the rapidly evolving nature of crypto taxation, investors should consult qualified tax professionals for specific situations and monitor regulatory developments continuously.
[27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43]
FAQ — Cryptocurrency Tax Guide 2025
Which countries offer 0% tax on crypto?
What is OECD CARF and when does it start affecting investors?
Which crypto actions are usually taxable?
How can investors legally optimize crypto taxes in 2025?
- Holding-period arbitrage — plan disposals after >12 months where eligible (e.g., Germany/Portugal).
- Residency planning — establish genuine tax residency in 0% or favorable regimes (e.g., UAE) before major exits.
- Loss harvesting & wallet segregation — realize losses to offset gains (where allowed) and separate wallets by activity (staking, trading, long-term).
What records should I keep for compliance?
Note: This is educational, not tax advice. Laws change quickly—consult a qualified professional for your situation.
Next step: turn insights into signals
- Bookmark our Tools & Dashboards (ETF flows, CME basis, BTC.D, stablecoins).
- Get weekly OSINT briefs + new panels: Subscribe Free.
- Explore more guides: Stablecoin flows • CME basis • ETH/BTC
Source
- https://coincub.com/europe-crypto-tax-guide/ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://cointelegraph.com/news/countries-where-crypto-is-tax-free ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://gordonlaw.com/learn/crypto-taxes-how-to-report/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.ird.govt.nz/international-tax/exchange-of-information/crypto-asset-reporting-framework ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.taina.tech/resources-news-and-awards/48-jurisdictions-commit-to-implement-the-crypto-asset-reporting-framework-carf-by-2027?_nodeTranslation=296 ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/middle-east/uae-new-crypto-tax-rules-2025-complete-guide-to-reporting-compliance-and-smart-tax-savings/articleshow/124028111.cms ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://koinly.io/blog/crypto-tax-free-countries/ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.globalcitizensolutions.com/crypto-tax-haven/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.dineshaarjav.com/blog-detail/crypto-tax-reality-check-2025 ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.careyolsen.com/insights/briefings/introducing-carf-oecds-crypto-asset-reporting-framework ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.globalcitizensolutions.com/portugal-crypto-tax/ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://nomadcapitalist.com/finance/cryptocurrency/germany-crypto-tax/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://coinledger.io/guides/crypto-tax-germany ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.blockpit.io/tax-guides/crypto-tax-united-kingdom-hmrc ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://cryptotaxcalculator.io/uk/guides/the-ultimate-defi-tax-guide-us ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://cointelegraph.com/explained/what-really-drives-altcoin-seasons-a-closer-look ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.binance.com/en-IN/square/post/29720909960874 ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://coinledger.io/blog/cryptocurrency-tax-rates ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://cardinalpointwealth.com/2025/07/29/cross-border-financial-planning-for-cryptocurrency-holdings-a-canada-u-s-guide/ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://coinledger.io/blog/crypto-tax-form ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.cryptact.com/en/blog/crypto-tax-free-country-top-crypto-friendly-nations-2025-guide ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://cryptotaxcalculator.io/de/guides/crypto-tax-germany ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://www.mme.ch/en/magazine/articles/automatic-exchange-of-information-on-crypto-assets ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://coinledger.io/guides/dubai-crypto-tax ↩︎ ↩︎ ↩︎
- https://dubaishift.com/best-uae-freezones-for-crypto-licenses-in-2025/ ↩︎
- https://koinly.io/guides/crypto-taxes/ ↩︎
- https://coinlaw.io/global-cryptocurrency-taxation-policies-statistics/ ↩︎
- https://taxsummaries.pwc.com/quick-charts/capital-gains-tax-cgt-rates ↩︎
- https://coredo.eu/countries-with-zero-cryptocurrency-tax-in-2025/ ↩︎
- https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/cryptoasset-reporting-framework/implementation-of-the-cryptoasset-reporting-framework-carf ↩︎
- https://www.blockpit.io/tax-guides/crypto-tax-guide-switzerland ↩︎
- https://www.oecd.org/content/dam/oecd/en/topics/policy-issues/tax-transparency-and-international-co-operation/faqs-crypto-asset-reporting-framework.pdf ↩︎
- https://www.oecd.org/en/publications/crypto-asset-reporting-framework-xml-schema-july-2025_6e60235b-en.html ↩︎
- https://immigrantinvest.com/blog/crypto-tax-havens/ ↩︎
- https://www.oecd.org/content/dam/oecd/en/networks/global-forum-tax-transparency/commitments-carf.pdf ↩︎
- https://www.astons.com/blog/top-10-crypto-friendly-countries/ ↩︎
- https://www.irs.gov/filing/digital-assets ↩︎
- https://www.paulhastings.com/insights/crypto-policy-tracker/crypto-tax-update-april-2025 ↩︎
- https://www.irs.gov/forms-pubs/about-form-8949 ↩︎
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/bc2e228edb096315fccfee088778465c/8734f2d2-de10-49b0-a79e-320ec701b52f/872a21c4.csv ↩︎
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/bc2e228edb096315fccfee088778465c/8734f2d2-de10-49b0-a79e-320ec701b52f/25f80b9b.csv ↩︎
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/bc2e228edb096315fccfee088778465c/8734f2d2-de10-49b0-a79e-320ec701b52f/ad42a365.csv ↩︎
- https://ppl-ai-code-interpreter-files.s3.amazonaws.com/web/direct-files/bc2e228edb096315fccfee088778465c/8734f2d2-de10-49b0-a79e-320ec701b52f/6c23d87e.csv ↩︎